Understanding Hyperthyroidism: When Your Thyroid Works Overtime
Feeling a bit like your body is running a marathon even when you're just sitting still? Perhaps you've noticed your heart racing, or maybe you're losing weight without trying. These sensations, you know, can be quite unsettling. It's almost as if your internal engine has shifted into a higher gear, and it's not slowing down. Well, this could be a sign of something called hyperthyroidism, a condition that really gets your body's systems moving at an unusual pace.
This condition, sometimes called an overactive thyroid, occurs when your thyroid gland, a small but mighty organ in your neck, produces and releases too much thyroid hormone. This hormone, thyroxine, is very important for how your body uses energy. When there's an excess, it speeds up several bodily functions, causing a whole range of noticeable symptoms. So, it’s about a gland that’s just a little too enthusiastic.
Many people find themselves wondering about these changes, and it's quite natural to seek answers. Understanding what hyperthyroidism is, what might cause it, how it's identified, and what can be done to manage it, is very helpful. This article aims to shed some light on this common thyroid disorder, giving you a clearer picture of what's happening and what steps you might consider. After all, knowing more can bring a sense of calm, you see.
Table of Contents
- What is Hyperthyroidism?
- Common Signs and Symptoms
- What Causes an Overactive Thyroid?
- Getting a Diagnosis
- Managing and Treating Hyperthyroidism
- Frequently Asked Questions About Hyperthyroidism
- Next Steps for Your Health
What is Hyperthyroidism?
Hyperthyroidism, simply put, means your thyroid gland is making too much thyroid hormone. This condition also is called an overactive thyroid, which sort of paints a picture of what’s going on. It happens when your thyroid, which is a butterfly-shaped gland located at the base of your neck, makes and releases high levels of this hormone. This excess hormone then circulates throughout your body, you know.
When your thyroid is overactive and produces too much of a hormone called thyroxine, it means your system is getting more signals than it needs. This leads to what is characterized by hypermetabolism, meaning your body’s processes are sped up beyond their normal rate. It's like having your car’s engine constantly revving, even when it should be idling. This can affect nearly every part of you, so it's a pretty big deal.
The disease itself is a common thyroid disorder with multiple underlying reasons why it might happen. This condition is marked by an excessive production of thyroid hormone, which then leads to elevated levels of free thyroid hormones in your blood serum. You may also hear the term thyrotoxicosis, which means there is too much thyroid hormone in your system, regardless of the cause. That, in a way, is what it's all about.
- Ynw Melly Mugshot
- Golden Retriever Puppy Siblings Tired
- Ei Ei Ei
- Coctel De Frutas
- Cómo Se Dice En Inglés Hola
Common Signs and Symptoms
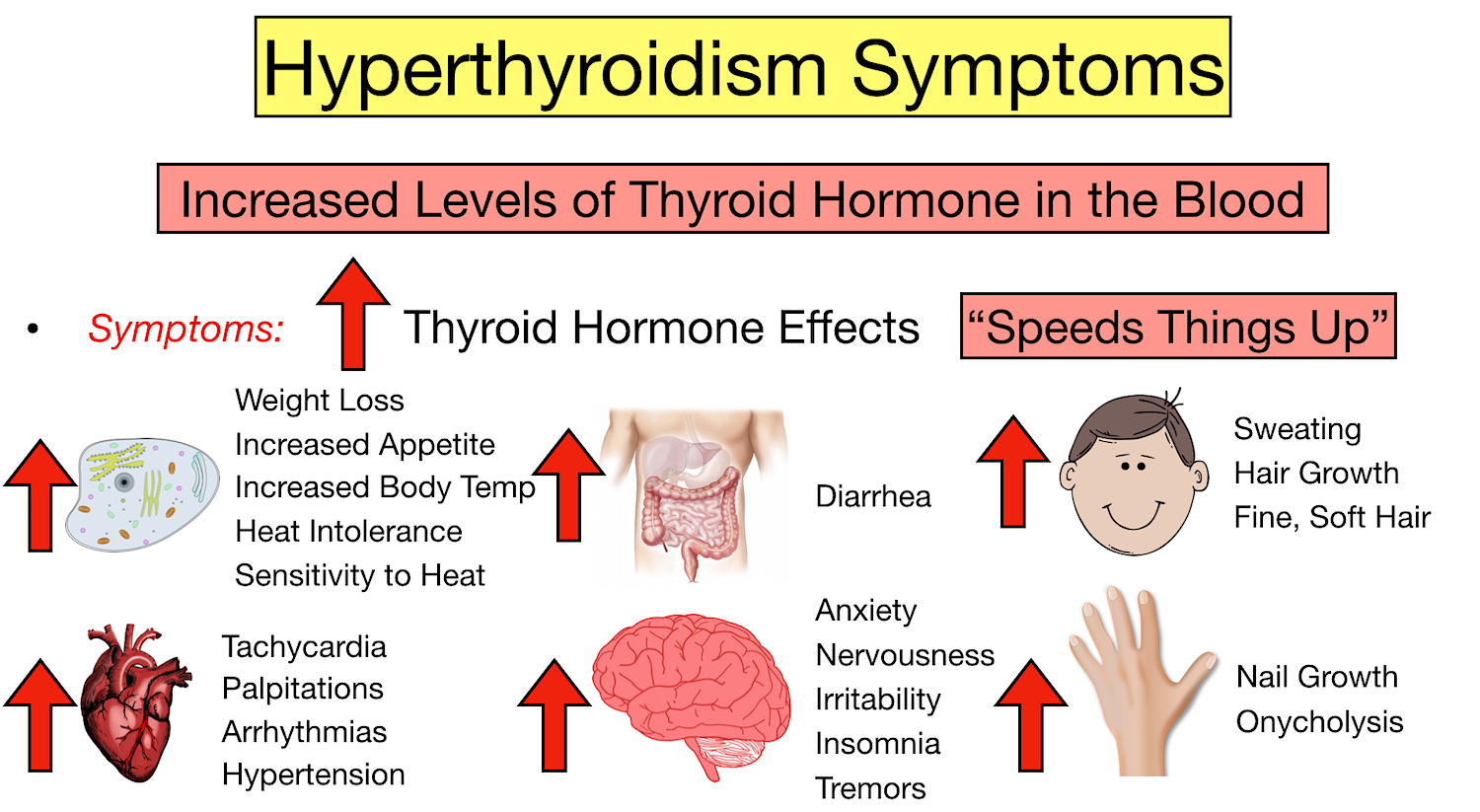
Because hyperthyroidism speeds up several bodily functions, it causes a variety of symptoms. These can show up in many different ways, making it sometimes a little tricky to pinpoint at first. Your body’s systems are, you know, just running faster than they should. This can lead to some rather noticeable changes in how you feel day to day.
One of the most common signs is weight loss, even if you’re eating the same amount or even more food. Your metabolism is so much faster, that your body burns through calories at an accelerated rate. You might also experience palpitations, which are feelings of a rapid or irregular heartbeat. It’s almost like your heart is trying to jump out of your chest, you see.
Fatigue is another frequent complaint, which might seem strange given the "speeding up" effect. However, the constant overactivity can really wear your body out. Heat intolerance is also common; you might feel hot when others are comfortable, or sweat more easily. Anxiety and nervousness can also be very present, as your nervous system is on high alert. Your hands might even tremble a little, so it's quite a wide range.
Other signs could include changes in your sleep patterns, like difficulty falling asleep, or feeling restless. Your skin might feel warm and moist, and your hair could become more fine or brittle. Muscle weakness, especially in your upper arms and thighs, can also develop. For some, there might be changes in bowel habits, like more frequent bowel movements. It’s a very systemic kind of issue, actually.
Sometimes, people notice changes in their eyes, such as puffiness around the eyes or a staring gaze. This particular symptom is more common with a specific cause of hyperthyroidism, but it’s worth noting. The symptoms can really vary from person to person, so what one person experiences might be quite different from another. That is just how it goes sometimes, you know.
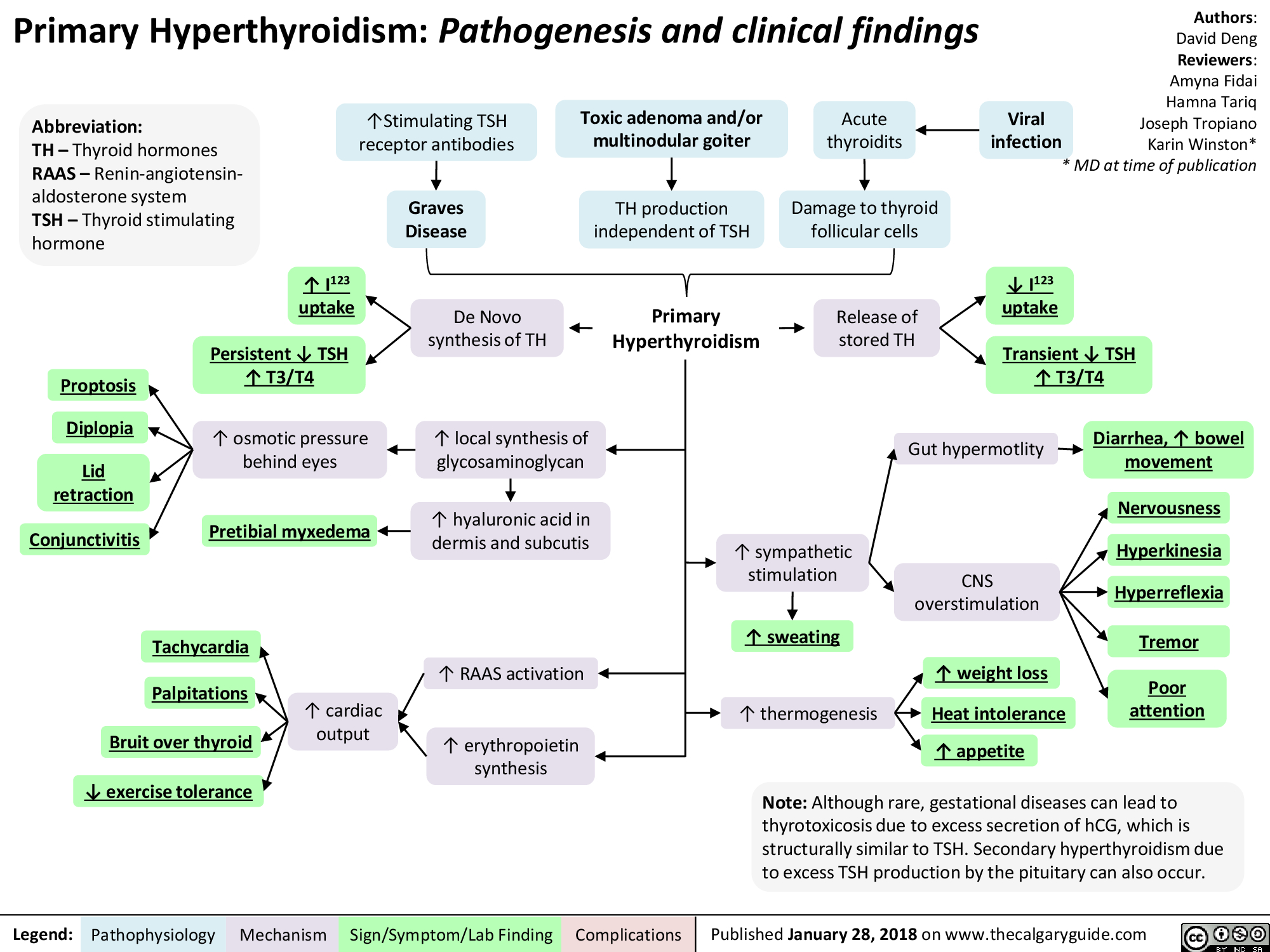
What Causes an Overactive Thyroid?
Hyperthyroidism, as we've discussed, means the thyroid gland makes too much thyroid hormone. But what makes it do that? There are several reasons why this might happen, and understanding the underlying causes is pretty important for figuring out the best path forward. It's not just one single thing, you see.
The most common cause is an autoimmune condition called Graves' disease. In this situation, your body's immune system, which normally protects you from germs, mistakenly attacks your thyroid gland. This attack causes the thyroid to become overstimulated and produce too much hormone. It’s a bit like your body’s defense system getting its wires crossed, actually.
Another cause can be thyroid nodules, which are lumps that form within the thyroid gland. Sometimes, these nodules can become "hot" or toxic, meaning they start producing their own thyroid hormone independently of the body's usual controls. These are often called toxic adenomas or multinodular goiters, and they can really contribute to the problem. It's a rather direct way for the gland to overproduce.
Inflammation of the thyroid gland, known as thyroiditis, can also lead to temporary hyperthyroidism. This happens when the inflamed thyroid leaks stored thyroid hormone into the bloodstream. This type of hyperthyroidism is often followed by a period of hypothyroidism, where the thyroid becomes underactive, as it recovers. So, it's a bit of a rollercoaster, in some respects.
Taking too much thyroid hormone medication, if you are being treated for an underactive thyroid (hypothyroidism), can also cause hyperthyroidism. This is why careful monitoring of medication levels is very important. It’s about finding that just-right balance, you know. Sometimes, even certain medications for other conditions can affect thyroid function, so it's worth considering everything.
Less common causes might include excessive iodine intake, which can stimulate the thyroid in some people, or certain rare tumors. Knowing the specific reason behind an overactive thyroid helps your healthcare provider determine the most effective way to help you. It’s really about getting to the root of the issue, that is what it's all about.
Getting a Diagnosis
If you're experiencing symptoms that suggest your thyroid might be overactive, getting a proper diagnosis is the next crucial step. Our expert endocrinologists, for instance, are skilled at finding out exactly what’s going on. They really know their stuff when it comes to hormone systems. It's about putting the pieces together, you see.
The diagnostic process usually begins with a thorough physical examination and a discussion about your symptoms and medical history. Your doctor will likely feel your neck to check the size and texture of your thyroid gland. They might also look for other physical signs, like changes in your eyes or tremors in your hands. This initial check-up is quite important, actually.
Blood tests are the primary way to confirm hyperthyroidism. These tests measure the levels of thyroid hormones, specifically thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), as well as thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH). In hyperthyroidism, you'll typically see high levels of T3 and T4, and a very low or undetectable level of TSH. This is because the high levels of thyroid hormone signal the pituitary gland to stop making TSH, which normally tells the thyroid to produce more hormone. It's a clear indicator, you know.
Sometimes, additional tests might be needed to determine the exact cause of the hyperthyroidism. A radioactive iodine uptake (RAIU) test, for example, can show how much iodine your thyroid gland takes up. A high uptake suggests Graves' disease or toxic nodules, while a low uptake might point to thyroiditis. This test helps distinguish between different reasons for the overactivity, which is very helpful.
An ultrasound of the thyroid gland might also be performed. This imaging test helps visualize the thyroid's structure, identify any nodules, and assess blood flow within the gland. It’s a non-invasive way to get a closer look at the thyroid itself. All these tests together help your healthcare team get a complete picture and confirm the diagnosis. So, it’s a pretty comprehensive approach.
Managing and Treating Hyperthyroidism
Once hyperthyroidism is diagnosed, there are several effective treatment options available to help manage the condition and bring your thyroid hormone levels back into balance. The goal is to reduce the amount of thyroid hormone your body is making, or to block its effects. It's about getting your body to slow down that accelerated pace, you know.
One common approach involves antithyroid medications, such as methimazole or propylthiouracil. These medicines work by reducing the thyroid gland's ability to produce hormones. They don't cure the condition, but they can effectively control the symptoms. Patients usually take these medications for a period of time, and some might even achieve a long-term remission. It's a good starting point for many, actually.
Another treatment option is radioactive iodine therapy. This involves taking a pill that contains a small dose of radioactive iodine. The thyroid gland naturally absorbs iodine, so the radioactive iodine goes directly to the overactive thyroid cells and destroys them. This reduces the amount of hormone the thyroid can produce. It's a very effective treatment, and it often leads to a permanent reduction in thyroid function, sometimes resulting in hypothyroidism, which is then easier to manage with daily medication. So, it's a trade-off, in a way.
Surgery to remove part or all of the thyroid gland, known as a thyroidectomy, is also an option. This is usually considered for people who can't take antithyroid medications, don't want radioactive iodine therapy, or have a very large goiter. After surgery, most people will need to take thyroid hormone replacement medication for the rest of their lives. It's a more permanent solution, you see.
Beta-blockers are often used to help manage the immediate symptoms of hyperthyroidism, like a rapid heart rate, tremors, and anxiety. These medications don't affect thyroid hormone production, but they provide relief from the uncomfortable symptoms while other treatments take effect. They can make you feel much better quite quickly, which is very helpful.
The choice of treatment depends on several factors, including your age, the cause of your hyperthyroidism, the severity of your symptoms, and your personal preferences. Your healthcare provider will discuss all the options with you to help you choose the best path forward. It’s a very personalized decision, you know. To learn more about thyroid health and how it impacts your well-being, visit our site. Finding the right treatment is key to feeling better and getting your life back on track, and our team is here to support you. You can also find more detailed information on various endocrine diseases on our dedicated pages.
Managing hyperthyroidism is about finding that right balance for your body. It might take some time and adjustments to medication, but with proper care, most people can lead full, healthy lives. Regular follow-up appointments are very important to monitor your thyroid hormone levels and adjust treatment as needed. It's a journey, in a way, but one with a clear destination of better health. For more general health information, you might find resources like NIDDK quite useful.
Frequently Asked Questions About Hyperthyroidism
What is the main cause of hyperthyroidism?
The main cause of hyperthyroidism is often an autoimmune condition called Graves' disease. In this situation, your body's immune system mistakenly causes the thyroid gland to produce too much hormone. Other causes can include thyroid nodules or inflammation of the thyroid gland, so it's not just one thing, you know.
What are the most common symptoms of an overactive thyroid?
Common symptoms of an overactive thyroid include weight loss despite eating normally, a rapid heartbeat, feeling tired, and being sensitive to heat. You might also experience anxiety, nervousness, or trembling hands. These are some of the more noticeable changes people report, you see.
How is hyperthyroidism typically treated?
Hyperthyroidism is typically treated with antithyroid medications to reduce hormone production, radioactive iodine therapy to destroy overactive thyroid cells, or surgery to remove part or all of the thyroid gland. Beta-blockers can also help manage symptoms. The best treatment really depends on your specific situation, you know.
Next Steps for Your Health
Living with hyperthyroidism can present challenges, but with the right information and medical care, managing the condition is very much possible. Understanding what it is, recognizing the signs, and knowing your treatment options are all crucial steps. It's about empowering yourself with knowledge, you know.
If you suspect you might have an overactive thyroid, or if you've been diagnosed and have questions about your treatment plan, reaching out to a healthcare professional is your best course of action. They can provide personalized advice and guide you toward feeling better. Taking charge of your health, you see, is a powerful thing.

Detail Author 👤:
- Name : Dianna Kertzmann
- Username : keyshawn.hermiston
- Email : trice@gmail.com
- Birthdate : 2005-11-22
- Address : 2124 Medhurst Glen East Litzyshire, NM 74452-2435
- Phone : 1-283-780-1680
- Company : Rogahn and Sons
- Job : Gaming Manager
- Bio : Vero esse nihil vel et aut eos. Esse exercitationem aliquam ut optio omnis. Quod sit quisquam aut suscipit impedit sint mollitia.
Socials 🌐
linkedin:
- url : https://linkedin.com/in/vernice_paucek
- username : vernice_paucek
- bio : Et natus et qui ipsa eos et.
- followers : 636
- following : 326
instagram:
- url : https://instagram.com/vernice_paucek
- username : vernice_paucek
- bio : Consequatur error quibusdam ex beatae. Odio vero rerum est. Minus hic minima cumque nam.
- followers : 4849
- following : 2238
tiktok:
- url : https://tiktok.com/@vernicepaucek
- username : vernicepaucek
- bio : At sed similique minima asperiores aspernatur.
- followers : 5695
- following : 2014
